Monday, December 07, 2009
The hidden costs of identity theft

Debra Guenterberg doesn't have to go to a horror movie to get spooked. She says she's been living a nightmare for the past 13 years.
The Wisconsin woman says she's been stalked by two phantoms. Two men stole her name and her husband's Social Security number. They used the information to obtain credit cards, buy cars and three homes.
Like many horror movie villains, the bad guys keep coming back. Thirteen years after the men stole their names, the Guenterbergs are still being turned down for credit because of the damage done by the men, she says.
Friday, December 04, 2009
Nationwide balloon-hunt contest tests online networking

The DARPA Network Challenge calls on groups to pinpoint the locations of 10 red weather balloons scattered around the country -- with a $40,000 prize going to the first team to find them all. DARPA, which stands for Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency, is the U.S. military's research arm.
This year's contest is designed to test the the way social networking, crowdsourcing or lesser-known Web-based techniques can help accomplish a large-scale, time-critical task.
Thursday, December 03, 2009
Wednesday, December 02, 2009
Racist Obama image shines light on Web searching

Google placed an ad near the image, apologizing for its offensive nature. But the company resisted calls to scrub the image from its database, saying its role as a neutral tool for searching the Web means having to live with the results, whether it likes them or not.
"We have a bias toward free expression," Google spokesman Scott Rubin told CNN. "That means that some ugly things will show up."
Tuesday, December 01, 2009
Activist's Web site, tweets put new face on homelessness
"I was sitting by the Chinese theater with my iguana, surrounded by Asian tourists, with my head down, thinking, 'How am I going to get out of this?' " said Horvath, whose nickname was the "Lizard Man of Hollywood Boulevard."
Last month, Horvath returned to Hollywood Boulevard, this time as a featured speaker at the 140 Characters Conference, a Twitter-inspired gathering attended by movers and shakers in social media. Horvath told the audience how he uses an arsenal of social networking sites -- Twitter, Facebook, Whrrl, MySpace, YouTube, Vimeo and Flickr -- to illuminate the plight of the nation's homeless.
Monday, November 30, 2009
Friday, November 27, 2009
An e-reader shortage for the holidays?

It seemed like this was going to be the holiday shopping season of the e-reader.
But that was before Barnes & Noble told customers it had run short on pre-orders of its new electronic book reader, the Nook. That device was poised to be a big holiday competitor to the more-established Amazon Kindle.
Barnes & Noble says customers who pre-order the Nook now won't get the device until the week of January 4 - after the holiday shopping season. A limited number of the devices will be available for sale in some of the "highest volume" Barnes & Noble stores.
In an e-mail, spokeswoman Mary Ellen Keating said early sales of the Nook beat the bookseller's expectations.
Thursday, November 26, 2009
Jet-powered Ford guns for 300 mph

Joe Wilkins knew there was only one way to give his supercharged, alcohol-injected Hemi-engined hot rod more power: Put a jet engine in the trunk.
"It started as a hobby and turned into a monster," said Joe Wilkins, the motor madman behind what might be the wildest 1939 Ford ever built. He's an inventor and defense department contractor, and the idea of goosing the Ford's ability to turn heads and shred tires came when he bought a used gas turbine engine.
"I got hooked on the simplicity and power that this thing produced, and I decided one day I want to put it in a car."
Wednesday, November 25, 2009
Is your date a 'stud or dud?' Ask your phone
Designers at a pair of companies say their new applications for smartphones can tell you in real time whether someone is married or divorced, has a criminal record, has filed for bankruptcy or has any number of potential red flags in their past.
Using Google to search for information on a prospective romantic partner is standard practice for many single people in the digital age. But these new apps, combined with the growth of smartphones and wireless networks, now allow for quick background checks on the go, potentially before a date is even over.
Tuesday, November 24, 2009
Hot video games for holiday shopping

But for non-gamers, navigating the many offerings at your local store can be confusing. So with that in mind, here are suggestions, grouped by category, on some of the most buzzed-about games for holiday giving.
Make sure you know which gaming console (PlayStation, Xbox, Wii) your gamer has before you shop. Prices for these games will range from $30 to $60, depending on the store and any promotions or sales. Check online or at your local store for the latest pricing.
These are only a few of the games in demand this holiday season. If you have other recommendations, feel free to let us know in the comments area at the bottom of this story.
For More Informatio
Monday, November 23, 2009
Fossil fuel chemicals avoided in plastics by Koreans

A team of South Korean scientists have produced the polymers used for everyday plastics through bioengineering, rather than through the use of fossil fuel-based chemicals.
It is believed that the technique may now allow for the production of environmentally-friendly plastic that is biodegradable and low in toxicity.
The research focused on Polylactic Acid (PLA), a bio-based polymer which holds the key to producing plastics through natural and renewable resources. Polymers are molecules found in everyday life in the form of plastics and rubbers.
"The polyesters and other polymers we use everyday are mostly derived from fossil oils made through the refinery or chemical process," Professor Sang Yup Lee, who lead the research, said in a press statement.
"The idea of producing polymers from renewable biomass has attracted much attention due to the increasing concerns of environmental problems and the limited nature of fossil resources. PLA is considered a good alternative to petroleum-based plastics, as it is both biodegradable and has a low toxicity to humans."
Until now PLA has been produced in a two-step fermentation and chemical process of polymerization, which is both complex and expensive. The team used a metabolically engineered strain of E. coli and developed a one-stage process.
"By developing a strategy which combines metabolic engineering and enzyme engineering, we've developed an efficient bio-based one-step production process for PLA and its copolymers," said Lee.
"This means that a developed E. coli strain is now capable of efficiently producing unnatural polymers, through a one-step fermentation process.
"Global warming and other environmental problems are urging us to develop sustainable processes based on renewable resources.
"This new strategy should be generally useful for developing other engineered organisms capable of producing various unnatural polymers by direct fermentation from renewable resources."
The research team from KAIST University in Seoul and the Korean chemical company LG Chem published their findings in the journal "Biotechnology and Bioengineering".
Friday, November 20, 2009
The New OS by Google

With a strong focus on speed, the Chrome OS promises nearly instant boot times of about 7 seconds for users to login to their computers.
"We want Google Chrome OS to be blazingly fast ... to boot up like a TV," said Sundar Pichai, vice president of product management for Google.
The first Chrome OS netbooks will be available in late 2010, Pichai said. It will not be available as a download to run and install. Instead, Chrome OS is only shipping on specific hardware from manufacturers Google has partnered with. That means if you want Chrome OS, you'll have to purchase a Chrome OS device.
Google is currently working with unnamed computer manufacturers to define specifications for these computers, which Pichai said will include larger netbook-style computers with full-size keyboards, large trackpads and large displays.
Chrome OS netbooks will not have traditional hard disk drives -- they will rely on non-volatile flash memory and Internet-based storage for saving all of your data.
All the applications will be web-based, meaning users won't have to install apps, manage updates or even backup their data. All data will be stored in the cloud, and users won't even have to bother with anti-virus software: Google claims it will monitor code to prevent malicious activity in Chrome OS web apps.
"Chrome OS is a totally rethought computer that will let you focus on the Internet, so you can stop worrying about your computer," according to a Google promotional video shown at the event, held at the Google campus in Mountain View, California.
As part of its announcement today, Pichai said that Google would be releasing all of the operating system's code and design documents to the public.
Introduced in July, Chrome OS is a Linux-based, open-source operating system centered on Google's Chrome browser. Applications will run exclusively inside the browser, Google said Thursday.
"As of today, the code will be fully open, which means Google developers will be working on the same tree as open developers," said Pichai.
The OS's focus on design is consistent with the company's stance that the future is in the web. In July, Vic Gundotra, Google's engineering vice president and developer evangelist, spoke on a panel about app stores, in which he said native apps (such as those available for the iPhone) would be obsolete in the future, and that the Web will "become the platform that matters."
"Every capability you want today, in the future it will be written as a web application," Pichai said Thursday.
Netbooks -- lightweight, low-powered sub-notebooks -- were the surprise hit of 2008 and 2009. However, with the growth of netbook sales slowing -- and the prices of some full-powered notebooks dropping below $400 -- the continued viability of the netbook sector is an open question.
Though netbook shipments are falling below manufacturers' expectations, the inexpensive, low-powered devices appear to still be selling well. Pichai cited research figures from ABI research indicating that 35 million netbooks shipped in 2009, more than twice the number sold in 2008.
Manufacturers have yet to announce pricing on netbooks shipping with Chrome OS, but Google expects the cost to be about the same as current netbooks. On average, netbooks cost between $300 and $500.
Videos demonstrating Chrome OS's user interface, security, fast boot and other features are below the jump.
Wednesday, November 18, 2009
Solar Photovoltaic Technology

Solar cells, also called photovoltaic (PV) cells by scientists, convert sunlight directly into electricity. PV gets its name from the process of converting light (photons) to electricity (voltage), which is called the PV effect. The PV effect was discovered in 1954, when scientists at Bell Telephone discovered that silicon (an element found in sand) created an electric charge when exposed to sunlight. Soon solar cells were being used to power space satellites and smaller items like calculators and watches. Today, thousands of people power their homes and businesses with individual solar PV systems. Utility companies are also using PV technology for large power stations.
Solar panels used to power homes and businesses are typically made from solar cells combined into modules that hold about 40 cells. A typical home will use about 10 to 20 solar panels to power the home. The panels are mounted at a fixed angle facing south, or they can be mounted on a tracking device that follows the sun, allowing them to capture the most sunlight. Many solar panels combined together to create one system is called a solar array. For large electric utility or industrial applications, hundreds of solar arrays are interconnected to form a large utility-scale PV system.
Traditional solar cells are made from silicon, are usually flat-plate, and generally are the most efficient. Second-generation solar cells are called thin-film solar cells because they are made from amorphous silicon or nonsilicon materials such as cadmium telluride. Thin film solar cells use layers of semiconductor materials only a few micrometers thick. Because of their flexibility, thin film solar cells can double as rooftop shingles and tiles, building facades, or the glazing for skylights.
Third-generation solar cells are being made from variety of new materials besides silicon, including solar inks using conventional printing press technologies, solar dyes, and conductive plastics. Some new solar cells use plastic lenses or mirrors to concentrate sunlight onto a very small piece of high efficiency PV material. The PV material is more expensive, but because so little is needed, these systems are becoming cost effective for use by utilities and industry. However, because the lenses must be pointed at the sun, the use of concentrating collectors is limited to the sunniest parts of the country.
Monday, November 16, 2009
New Technology Prolongs Produce Freshness
Nutritionists encourage eating a healthy diet rich in fresh fruits and vegetables. In response, consumers flock to their grocery stores and stock up these healthful foods. Too often, though, produce spoils soon after purchase. This is becoming more common as more produce is imported from around the world.
The cause of the untimely spoilage is ethylene, a plant hormone that fruits and vegetables produce naturally as they ripen. Even at temperatures colder than 39° Fahrenheit, apples and avocados produce high quantities of ethylene. The situation is complicated when fruits and vegetables are packaged for long trips—as the air in the confined container circulates, the concentration of ethylene gas, even as low as .01 parts per million, accelerates the ripening of stored produce.
Postharvest losses due to spoilage, estimated at 30 to 40 percent worldwide, affect the economic success of growers, packers, storage houses, and distributors of produce.
With funding from USDA’s Cooperative State Research, Education, and Extension Service (CSREES), Dr. Reza Shekarriz and W. L. Allen of Fluid Analytics, Inc., in Lake Oswego, Ore., have developed a compact sensor to accurately measure low concentrations of ethylene on transport containers.
“This issue is becoming more critical as global trade and year-round consumption of fresh fruits and vegetables increases,” Shekarriz said. “Ethylene-related problems make up a significant portion of postharvest losses in developing countries, resulting in negative economic impacts worth billions of dollars every year.”
Produce freshness can be controlled by carefully monitoring and regulating exposure to ethylene during transport. Reducing produce exposure to ethylene slows the natural ripening process, thereby extending produce shelf life.
The new sensor continuously samples air at a regulated flow rate, normally 12 to 30 cubic inches of air per minute. Not only can the sensor detect ethylene at concentrations low enough to ripen produce, it also reports ethylene concentration in real-time to provide greater control over ethylene levels during transport.
“This sensor is far more sensitive to ethylene detection than previous technology. Future developments may increase sensitivity to provide better response times and will be integrated with ethylene scrubbers to actively remove ethylene from cold storage rooms and shipping containers” said Shekarriz.
This device is particularly important for organic produce that does not use other chemicals to control the ripening process.
The beneficiaries of this new sensing technology include horticulture and floriculture research institutions, growers, packing houses, cold-storage facilities, greenhouses, shipping containers, and consumers.
Scientists in the United States, Germany, England, France, and the Netherlands are already using prototypes of the ethylene sensor. Future work by this research team will focus on developing new technology to remove ethylene from an enclosed space to further reduce the complications of postharvest ripening.
This technology has been licensed to a French company, ABSOGER, for commercialization into the European cold storage market. The commercial units are expected to reach the market in mid-2009.
Friday, November 13, 2009
Thermally Modified Wood
Thermally modified wood is produced by subjecting solid wood to high temperatures to improve their dimensional stability and biological durability. Solid wood is exposed t 160-240 oC in an atmosphere of low oxygen content or oil is used to transfer heat to the wood.
The wood’s properties can be altered by modifying its cell wall components using heat. Portions of hemicelluloses are hydrolyzed into to their monosaccharide components such as glucose, galactose, mannose, arabinose and xylose The amorphous regions of cellulose are also hydrolyzed, breaking cellulose into shorter chains. The degradation of the cell wall’s two major components leads to reduced free hydroxyl groups in the chemical structures and increased cross-linking of lignin.
The modifications result in several changes in the wood’s properties. The following are basic properties of thermally modified wood, regardless of the kind of thermal modification ™ process used: (1) decreased heat conductivity by 10 – 30%; (2) decreased mechanical strength by up to 30%; (3) reduced weight by 5 – 15%; (4) decreased shrinking and swelling by 50-90% due to reduced equilibrium moisture content of the wood; (5) improved biological durability; (6) extractives migration to the wood surface, and (7) color change from whit or yellow to dark brown.
Commercial production of thermally modified wood started in the late 1990’s in Europe. ThermoWood. PlatoWood, Retification and Perdure, and Oil-heated wood of Finland, Netherland, France and Germany, respectively, are some of the popular TM processes.
Green, air-dried and kiln dried wood can be thermally modified depending on the TM process used. For example, in the Finnish Thermowood process, green wood is first dried above 100 0c. Thermal modification follows after the desired moisture content of 10% is reached. The treatment temperature and duration will vary depending on the wood’s end-uses.
In 1974, FPRDI started conducting studies on thermal modification. Mailum and Arenas subjected five local wood species to different temperatures ( 130, 150 and 175 0C). Results showed improvement in the natural durability of acacia [Samanea saman (Jacq.) Merr.], guijo [Shorea guiso (Blanco) Blume], mayapis [Shorea palosapis (Blanco) Merr.] and palosapis {Anisoptera thurifera (Blanco) Blume spp. Thurifera] against two decay fungi species, i. e. Fomes liviudus, a white-rot fungus and Lenzies striata, a brown-rot fungus.
However, no similar studies followed thereafter until a 2009 research on plantation species, malapapaya [Polyscias nodosa (Blume) Seem.]. Malapapaya was thermally modified to improve its physico-mechanical properties and decay resistance using different combinations of temperature and treatment durations. Results showed significant improvement on the biological durability and dimensional stability, as well as color change in malapapaya wood.
Thursday, November 12, 2009
Wednesday, November 11, 2009
How To: Jailbreak 3.0 iPod Touch 1g & 2g, iPhone, iPhone 3g On Windows/Mac
Tuesday, November 10, 2009
New and Emerging Environmental Technology (NEET)
The NEET website is an on-line repository for information about technologies that prevent, remove, destroy, sample, monitor, or model air pollutant emissions from stationary, mobile, and indoor sources. NEET contains information about technologies for improving air quality that are commercially available, as well as technologies that are currently being developed. You use NEET's search features or the technology provider directory to find technologies listed in NEET that meet your needs.
All owners, manufacturers, developers, and research sponsors of air technologies are invited to list their technologies in the NEET database. Adding your technology is an easy on-line procedure that you perform with your own password-protected account. Your technology can be a commercially available technology or an emerging technology in research and development. Listing technologies is free.
Monday, November 09, 2009
Saturday, November 07, 2009
Thursday, November 05, 2009
Wednesday, November 04, 2009
Fuel injection
Fuel injection is a system for mixing fuel with air in an internal combustion engine. It has become the primary fuel delivery system used in gasoline automotive engines, having almost completely replaced carburetors in the late 1980s.
A fuel injection system is designed and calibrated specifically for the type(s) of fuel it will handle. Most fuel injection systems are for gasoline or diesel applications. With the advent of electronic fuel injection (EFI), the diesel and gasoline hardware has become similar. EFI's programmable firmware has permitted common hardware to be used with different fuels. Carburetors were the predominant method used to meter fuel on gasoline engines before the widespread use of fuel injection. A variety of injection systems have existed since the earliest usage of the internal combustion engine.
The primary difference between carburetors and fuel injection is that fuel injection atomizes the fuel by forcibly pumping it through a small nozzle under high pressure, while a carburetor relies on low pressure created by intake air rushing through it to add the fuel to the airstream.
The fuel injector is only a nozzle and a valve: the power to inject the fuel comes from a pump or a pressure container farther back in the fuel supply.
Tuesday, November 03, 2009
Industrial R&D Promotion Programme
Department of Scientific & Industrial Research (DSIR) is the nodal department for granting recognition to in-house R&D units in Industry, Scientific and Industrial Research Organizations (SIROs); and registration to Public funded research Institutions, universities, IIT’s, IISc, Regional Engineering College (RECs), other than hospitals.
Secretary, DSIR is the prescribed authority vide Gazette notification No.S.O.85 (E) dated 31st January, 2001 issued by Department of Revenue, Ministry of Finance for granting approval to commercial R&D companies Under Section 80IB (8A) of I.T. Act, 1961; also approval to in-house R&D Centres under Section 35(2AB) of I.T Act 1961 for Weighted Tax Deduction.
In-house R&D units recognized by DSIR in the area of pharmaceutical and bio-technology sector are eligible for duty free import of specified goods (comprising of analytical and specialty equipment as per list 28) for R&D as per notification No. 26/2003-customs dated 1st March, 2003 (item at Sl. No. 248(1); and duty free import of specified goods (comprising of analytical and specialty equipment as per list 28) for production as per notification No.26/2003-customs dated 1st March, 2003 (item at serial No.248(2); and duty free import of pharmaceutical reference standards as per notification No.26/2003-Customs dated 1st March, 2003 (item at serial No.138); and also the in-house R&D units engaged in the research and development in the area of chemical, drugs pharmaceuticals, (including clinical trials), bio-technology, electronic equipments, computers, telecommunication equipments, aircrafts and helicopters are eligible for weighted tax deduction of a sum of equal to one and one-half times of any expenditure incurred on scientific research (not being expenditure in the nature of cost of any land building) as approved by the prescribed authority i.e. Secretary, DSIR. In case of dispute, Secretary, DSIR is also prescribed authority in concurrence with Director General of Income-Tax (Exemption) for deciding cases of R&D expenditure made on Capital Equipment and related R&D activities under Section 35 of Income-Tax Act, 1961 referred by Central Board of Direct Taxes.
A few more incentives introduced by the Government to encourage R&D by industry include write off of revenue and capital expenditure on R&D, weighted tax deduction on sponsored research programmes of industry with National Laboratories/Universities /IITs; accelerated depreciation allowance on plant and machinery set up indigenous technology, custom duty exemption on goods imported for use in Government funded R&D projects, excise duty waiver for 3 years on goods produced based on indigenous technologies and duly patented in any two of the countries out of India, European Union(One Country), USA and Japan.
Scientific & Industrial Research Organizations in the area of Medical Agriculture, Natural and Applied Sciences and Social Sciences recognized by DSIR are eligible for notification under Section 35 (1) (ii)(iii) of I.T Act 1961 and also for availing Custom and Excise duty exemption.
Commercial R&D companies approved by DSIR before 1st April, 2004 are eligible for 10 years tax holidays.
Public Funded R&D Institutions registered by DSIR are eligible for availing custom duty exemption on import of equipment, spares and accessories and consumables as per notification No.51/96-Customs dated July, 23, 1996 and also for availing Central Excise Duty Waiver on purchase of indigenously manufactured items as per notification No. 10/97- Central Excise dated March 1, 1997 for scientific research purposes.
Objectives
* The broad objectives are to:
* Bring in-house R&D into sharper focus;
* Strengthen R&D infrastructure in industry and SIROs;
* Promote R&D initiatives of the industry and SIROs ;
Ensure that the contributions made by the in-house R&D centres and SIROs dovetail adequately in the overall context of technological & industrial development
Monday, November 02, 2009
Advanced Diamond Technologies
Formed in December 2003, ADT provides diamond film and materials integration solutions to a variety of industry participants in diverse application areas. It is based in Champaign, IL. Its website is www.thindiamond.com.
Friday, October 30, 2009
Thursday, October 29, 2009
Integrated Starter/Generator (ISG)
Wednesday, October 28, 2009
The Freaky F-35 Lid

The head gear being developed for the hi-tech F-35 Joint Strike Fighter is being tested by MoD scientists at Boscombe Down in Wiltshire.
An MoD spokesman said: "Unlike other jet aircraft the JSF, which is planned to replace the Harrier, does not have a traditional head-up display.
Instead the computerised symbology will be displayed directly on to the pilot's visors, providing the pilot with cues for flying, navigating and fighting the aircraft.
"It even will superimpose infra-red imagery on to the visor to allow the pilot to look through the cockpit floor at night and see the world below - like something out of Terminator.
"This is absolutely the cutting edge of technology. No other helmet will be able to do this."
The head gear, currently at prototype stage, is being developed by Vision Systems International and Helmet Integrated Systems Limited.
Tuesday, October 27, 2009
Human Research Program - Advanced Food Technology
AFT is responsible for developing food systems for space vehicles and long duration missions that use a combination of extended shelf life stored foods and raw food products produced from higher plants or bulk raw commodities. AFT research addresses nutritional, psychological, safety, and acceptability requirements, while minimizing mass, volume, power, waste and trace gas emissions. In doing so, the AFT must address different mission scenarios that present challenges beyond conventional knowledge concerning food.
The goals of the AFT are to:
- Develop a stored food system that is nutritious, palatable and provides a sufficient variety of foods to support significant crew activities on a mission of at least 3 years duration. Foods should maintain safety, acceptability, and nutrition for the entire shelf life of 3 - 5 years. Shelf life extension may be attained through new food preservation methods and/or packaging.
- Develop new packaging technologies to minimize waste from packaged food.
- Develop handling procedures for minimally processed vegetable crops.
- Develop equipment to process crops in reduced gravity that are highly automated, highly reliable, safe, and minimize crew time, power, water, mass, and volume.
- Develop recipes, galley operations, and galley equipment for extended surface missions.
Current activities of the AFT are concentrating on near term needs in order to augment the Shuttle and ISS food system while working towards an advanced food system. Activities include:
- Shelf life testing of thermally processed foods.
- Identification and testing of packaging materials with high barrier properties and low mass and volume.
- Investigation of emerging preservation technologies that wil provide extended shelf life food items with improved nutrition and acceptability.
Monday, October 26, 2009
Wild dog check fences
The wild dog check fences were built to protect animals in the adjacent cropping and grazing lands. Although the check fences do not physically link up with the wild dog barrier fence, they play an important role in wild dog control in southern Queensland.
Some sections of the Darling Downs-Moreton Rabbit Board fence are top-netted to wild dog-proof standard, and these form part of the check fences.
In 1984 the wild dog check fences were restored by the state government as part of the wild dog barrier fence restoration program. They were then handed over to local governments, with the agreement that they would oversee and fund the maintenance of the fences to a dog-proof standard. Most of the fences have been well maintained and have been improved from their original condition.
The map below shows the location of the check fences in relation to the wild dog barrier fence and the Darling Downs-Moreton Rabbit Board fence.
Saturday, October 24, 2009
Friday, October 23, 2009
Thursday, October 22, 2009
Tennis Racket Shapped Collector

When hypervelocity particles are captured in aerogel they produce narrow cone-shaped tracks that are hollow, and can easily be seen in the highly transparent aerogel by using a stereomicroscope. This cone is largest at the point of entry, and the particle is held intact at the point of the cone. This provides a method for determining which direction the dust came from, and is the basis of the approach of using single slabs of aerogel to collect both cometary and interstellar dust from both sides.
After the encounter with Comet Wild 2, the aerogel collector will be retracted into the Sample Return Capsule (SRC) and returned to Earth for detailed analysis by scientists at the NASAs Johnson Space Center.
Wednesday, October 21, 2009
A New Camera for Extrasolar Planets
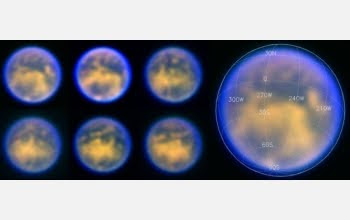
For the better part of a year, an international team of astronomers has been working with a powerful new camera that may soon yield the first images of planets in other solar systems—and already, it has made some significant discoveries.
The Simultaneous Differential Imager (SDI) was jointly built by the University of Arizona’s Laird M. Close, who is working under a five-year CAREER grant from the National Science Foundation, and by Rainer Lenzen of the Max Planck Institute of Astronomy in Heidelberg, Germany. Its first target was Saturn’s moon Titan: during the instrument’s commissioning run early last year at the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope in Chile, the astronomers obtained maps of Titan’s smog-shrouded surface that were almost as detailed as those made a few months later by the Cassini spacecraft. Shortly after, the researchers discovered a very rare, low-mass “brown dwarf binary” pair called Epsilon Indi Ba and Bb. Brown dwarfs are blobs of gas too small to shine like a star, but too big and warm to be called planets. Epsilon Indi Ba and Bb are only the third brown-dwarf pair known.
And then, as the astronomers described in the Jan. 20, 2005, issue of the journal Nature, SDI images of the very young star AB Doradus A revealed a brown dwarf companion having 93 times the mass of Jupiter, the largest planet in our own solar system—which makes this particular brown dwarf almost twice as heavy as theory predicted it should be based on its observed brightness.
“This discovery will force astronomers to rethink what the masses of the smallest objects produced in nature really are,” says Close.
In the meantime, he adds, the SDI team is continuing the search for actual planets, which are expected to be far dimmer than the brown dwarfs. That dimness is one big reason why no extrasolar planet has ever been imaged directly: they are lost in the glare of their parent stars. (The 120-plus extrasolar planets that have been found to date have all been detected indirectly, mostly through their effects on the motion of their parent stars.)
To eliminate this glare, the SDI first relies on its host telescope’s standard “adaptive optics” system to remove the blurring effects of Earth's atmosphere. Then the SDI takes the sharply focused light from a particular target star, and beams it into an internal optical system that is sensitive to light emitted by methane: a carbon compound thought to be abundant in the atmospheres of gas-giant planets. After some further computer processing, the result is a synthetic image in which the light from the star has been subtracted out, leaving nothing but the images of any faint, cool, methane-rich companions.
The SDI team has looked at about 20 stars so far, says Close, and the data are currently being analyzed—mainly by University of Arizona graduate student Beth Biller. “No confirmed planets yet,” he says, “but we should be able to detect planets some 20,000 times fainter than their primary star.”
Moreover, he says, the SDI’s direct imaging approach should nicely complement the standard method of looking for planets’ indirect effects on the parent star’s motion. “That technique is better for giant planets orbiting close in,” he says, “whereas ours should do better for giant planets like Jupiter or Saturn in our own solar system, which orbit further out.”
Tuesday, October 20, 2009
New Pacific Air Force Technologies Fly
The U.S. Pacific Air Forces are rolling out new technologies and capabilities to government and industry partners while seeking to consolidate for efficiencies. But, its vice commander bemoans continuing cultural and technological hurdles to effective network centricity.
Among the new capabilities are voice over secure Internet protocol (VoSIP), which is in four bases and will be installed in all nine bases over the next 12 months. Airmen also are receiving secure mobile personal digital assistants with Defense Information Systems Agency (DISA) security for sending secure e-mail. And, network operations and CERT functions are consolidated into single Air Force network operations.
But Maj. Gen. Mike Hostage III, USAF, vice commander, Pacific Air Forces, wants effective systems delivered on time. “A perfect course of action late to the fight isn’t as good as a 90-percent solution delivered on time,” he said. And, these systems should serve military needs, not those of industry.
The Army can provide ballistic missile defense capabilities to the Pacific Air Forces’ air operations center. This helps improved missile threat defense. But, this data must be displayed on a separate monitor. Gen. Hostage wants that data to be consolidated with Air Force data so it can appear on a common monitor.
And, industry needs to build solutions based on Air Force needs, not its own capabilities. Gen. Hostage told industry, “Show us what you’ve got, look at our problem set, then help draw the links between the two.”
Monday, October 19, 2009
Thursday, October 15, 2009
Electronic cigarette

An electronic cigarette or "e-cigarette" is a battery-powered device that provides inhaled doses of nicotine by heating a nicotine-chemical solution into a vapor. It is an alternative to smoked tobacco products, such as cigarettes, cigars, or pipes. In addition to nicotine delivery, this vapor also provides a flavor and physical sensation similar to that of inhaled tobacco smoke, while no tobacco, smoke, or combustion is actually involved in its operation.
An electronic cigarette usually takes the form of some manner of elongated tube, though many are designed to resemble the outward appearance of real smoking products, like cigarettes, cigars, and pipes. A common design is also the "pen-style", so named for its visual resemblance to a ballpoint pen.
Most electronic cigarettes are reusable devices with replaceable and refillable parts. A number of disposable electronic cigarettes have also been developed.
The legal status of electronic cigarettes varies by country.
Wednesday, October 14, 2009
Mobile Radio Data Technology
The MDRS network’s componentry is designed for easy location and installation. Its small, uncomplicated units consist of a Data Radio Base Station, the MX Data Network Switch and the NCC Network Control Centre.
This streamlined, modular architecture makes for an extremely efficient and flexible management regime. The network can be precisely configured to match a particular service mix and meet expected solution requirements. Then, as demand and service uptakes change over time, the network can be easily re-configured.
While MDRS bears some similarity to the digital cellular technology of today’s mobile phone systems, it is unique in several respects. Firstly, as a narrowband technology designed for wireless data communication, it uses packet switching to maximise spectrum efficiency. Secondly, it is a dedicated, data-only network that is based on an open, international standard.
This means, that over the greatest number of wireless data applications, MDRS is the most cost-effective technology.
In the field, MDRS can be relied upon to meet the requirements of public safety and business-critical applications. By ensuring that real time data is available onsite and on-demand, MDRS empowers its users to respond in a timely manner.
Tuesday, October 13, 2009
Monday, October 12, 2009
Computer Security Objects Register (CSOR)
Information objects that convey information used to maintain the security of resources in computerized environments are known as Computer Security Objects (CSOs). The Computer Security Objects Register (CSOR) specifies names that uniquely identify CSOs. These unique names are used to reference these objects in abstract specifications and during the negotiation of security services for a transaction or application. The CSOR is also a repository of parameters associated with the registered objects. For agencies requesting a new OID, please send email with OID name, associated document and point of contact information.
The CSOR is currently registering the following objects:
- Security Label
- Information Object Security Program
- Public Key Infrastructure
- Cryptographic Algorithm
New registration branches and their object-specific requirements will be defined as the need arises.
CSOR Documents
The following documents are referenced throughout this CSOR web site:
- Federal Information Processing Standards (FIPS)
- NIST Interagency Reports
- Secure Data Exchange (SDE) Security Label (802.10g - 1995)
- Defines the security label format for the IEEE802.10 Secure Data Exchange (SDE)
CSOR Disclaimer
The registration service presented here does not provide an endorsement or approval for techniques, algorithms, or products using the specifications maintained. Similarly, there is no explicit or implicit indication of the correctness or suitability of registered computer security objects for any use. Use of the Computer Security Objects Register (CSOR) is not mandatory, although recommended as a tool for achieving interoperability. Conflicts with ownership and/or rights over alpha-numeric object names and specifications must be resolved by applicants prior to the submission of a request for registration. The registration of a security object assigns the applicant no rights over the object or its name and is therefore no absolute proof of ownership. Registered objects and their names may be protected by copyrights and or patents and their use by others than the owner may require special arrangements without the involvement of the Registration Authority. Upon requesting registration, applicants give the Registration Authority permission to reproduce and distribute the names and specifications of all objects being registered.
Friday, October 09, 2009
Bar Code Technology
There are many different bar code symbologies, or languages. Each symbology has its own rules for encoding characters (e.g., letter, number, punctuation), printing, decoding requirements, and error checking.
Bar code symbologies differ both in the way they represent data and in the type of data they can encode: some encode numbers; others encode numbers, letters, and a few punctuation characters; still others offer encodation of the 128 or 256 ASCII character sets. Recently unveiled symbologies include options to encode characters in any language as well as specialized data types.
Bar codes in common use are covered by international standards. International standards also cover print quality measurements and equipment.
Bar code technology standards define:
- Rules for representing data in an optically readable format,
- Rules and techniques for printing or marking,
- Reading and decoding techniques, and
- Rules for measuring the quality of printed/marked symbols
Thursday, October 08, 2009
Wednesday, October 07, 2009
New Chemical Exposure Limits (NCELs)
Under section 5 of the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA), any person who intends to manufacture or import a new chemical substance in the United States for commercial purposes must submit a premanufacture notice (PMN) to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) at least 90 days prior to manufacture or import. EPA's Office of Pollution Prevention and Toxics (OPPT) performs a risk assessment and makes a risk management decision.
If EPA determines, among other things, that the PMN substance may present an unreasonable of injury to human health via inhalation exposure, EPA is likely to issue a TSCA section 5(e) Consent Order. The section 5(e) Order is likely to require, among other things, that potentially exposed employees of the Company must wear specified respirators unless actual measurements of the workplace air show that air-borne concentrations of the PMN substance are below a New Chemical Exposure Limit (NCEL) that is established by EPA to provide adequate protection to human health.
In addition to the actual NCEL concentration, the comprehensive NCELs provisions, which are modeled after Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) Permissible Exposure Limits (PELs), include requirements addressing performance criteria for sampling and analytical methods, periodic monitoring, respiratory protection, and recordkeeping. EPA generally extends these section 5(e) Order requirements to other manufacturers and processors of the same chemical substances via a section 5(a)(2) Significant New Use Rule (SNUR).
NCELs Table -- The NCELs Table lists the actual NCEL concentrations established by EPA for specific chemical substances regulated by section 5(e) Orders. The NCELs Table is intended to provide a convenient list of all NCELs established by EPA (up to the date of Internet posting). This list of NCELs concentrations is not published in the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) or elsewhere. To protect Confidential Business Information (CBI) under section 14 of TSCA, the NCELs Table gives generic descriptions of those PMN substances for which the company claimed the chemical identity as CBI.
Tuesday, October 06, 2009
Mobile Communication Technology for Adolescents With Diabetes
This study will investigate a novel cell phone glucose monitoring system (CPGM) with the following specific aims:
1. To establish feasibility of a CPGM system as a component of an adolescent diabetes management program.
2. To determine if the technology will improve a) quality of parent-child relationship, b) patient quality of life, c) competence in diabetes management, and d) metabolic control.
3. To gather preliminary data for development of future intervention studies.
120 adolescents with type I diabetes will be randomly assigned to either an experimental or control group.
Experimental subjects will use the CPGM which will transmit all blood glucose data to a host computer. A nurse practitioner in the pediatric endocrinology clinic will determine need for telephone contacts based on evaluation of transmitted data. Subjects might be telephoned to discuss possible regimen adjustments, need for clinic visits, or referrals to additional services. Subjects will also be able to initiate contact with the project nurse. Control subjects will continue to receive standard care. .
This study will assess the effect of the intervention in the four primary domains stated in the specific aims.
These domains will be measured at baseline, three months, and six months.
Monday, October 05, 2009
Friday, October 02, 2009
Vapour recovery at petrol service stations
In 2002, the Department of Environment and Climate Change (DECC) commenced evaluation of vapour recovery technology at service stations to reduce the emission of petrol vapours during refuelling of vehicles.
This technology is known as Stage 2 vapour recovery or 'VR2'. Over the last 20 years VR2 has been successfully introduced across the United States, Europe and in many parts of Asia to reduce local, regional and global air pollution.
In August 2007, DECC released a discussion paper seeking public comment on a proposal to expand vapour recovery at service stations in the Greater Metropolitan Region (GMR) of NSW.
As a result of this consultation, in November 2007 the State Government announced its intention to:
- expand the Stage 1 vapour recovery technology already in use at service stations in Sydney to the Central Coast, Illawarra and Lower Hunter
- phase in Stage 2 vapour recovery technology at service stations in the Sydney, Central Coast, Wollongong and Newcastle metropolitan areas.
Thursday, October 01, 2009
Wednesday, September 30, 2009
Nuclear Medicine Technologists
- Two-thirds of nuclear medicine technologists worked in hospitals.
- Nuclear medicine technology programs range in length from 1 to 4 years and lead to a certificate, an associate degree, or a bachelor’s degree.
- Faster-than-average job growth will arise from an increase in the number of middle-aged and elderly persons, who are the primary users of diagnostic and treatment procedures.
- The number of job openings each year will be relatively low because the occupation is small; technologists who also are trained in other diagnostic methods, such as radiologic technology or diagnostic medical sonography, will have the best prospects.
Tuesday, September 29, 2009
New Weather Technology Helps NOAA Storms Lab Develop Pilot Program
When a hurricane or severe storm hits North Carolina, South Carolina or Virginia - as Hurricane Floyd did in 1999 - weather forecasters now anticipate delivering more accurate flood and flash flood warnings.
Scientists are testing new advanced weather technology in a pilot program from the National Oceanic & Atmospheric Administration's (NOAA) National Severe Storms Laboratory (NSSL), NOAA's National Sea Grant College Program and North Carolina and South Carolina Sea Grant state programs.
New software that utilizes Doppler radar data, satellite imagery and other information tools will monitor rainfall in watershed basins as small as one square kilometer.
National Weather Service (NWS) forecasters can use the data to issue more precise and accurate flood and flash flood warnings. Emergency management officials, utility companies and others can use data to better prepare for flood events.
With new technology, researchers hope to mitigate losses such as the tremendous damage caused by Hurricane Floyd. In North Carolina, for example, the statistics were staggering - 52 deaths, 7,000 homes destroyed, 17,000 uninhabitable homes and 57,000 homes damaged.
"This will help save lives and protect property," said North Carolina Sea Grant marine educator Lundie Spence, who was one of several Sea Grant representatives who visited NSSL last year in an effort to develop joint projects within the two NOAA agencies.
"If we can assist the local NWS Forecast Office with implementation of new technology that provides additional details about a severe storm system, specific amounts of rainfall and the type of precipitation, people will have more opportunity to prepare to evacuate areas," Spence added.
The project has two phases: collecting regional radar data in "real time" at a single location at Wilmington, N.C., and creating Web-based flash flood guidance software using real time radar data.
The regional or multi-state images, which will be available by late September, will combine raw data from several National Weather Service Doppler radars in coastal North and South Carolina and coastal southern Virginia.
Currently, each NWS office can only get Doppler radar data from one or two radars at a time," said Kevin Kelleher, deputy director of the National Severe Storms Lab in Norman, Okla.
"With this new technology, we will be able to provide regional, multi-radar images and forecast products using realtime Doppler data to NWS forecasters and emergency managers extending from coastal Georgia to Washington, D.C.," Kelleher added.
"The ability to receive multi-sensor estimates of accumulated rainfall for individual river basins should really be helpful in managing flood situations."
By December, the second phase of the project will be nearly complete. Data will be available on the World Wide Web to a variety of users, including weather forecasters, emergency management officials, mariners, scientists and commercial users in the power and agricultural sectors. The data will include information on the amount of rainfall that has fallen in each river basin and an indication of the likelihood that flooding will occur.
"Web-based data will include color maps that will help emergency management officials more quickly and accurately identify the areas at greatest risk for flood," said South Carolina Sea Grant extension program leader Robert Bacon. "For example, they can more effectively target areas for evacuation and position their response and recovery resources to assist flood victims."
The National Sea Grant Program is a university-based program that promotes the wise use and stewardship of coastal and marine resources through research, outreach and education.
Thursday, September 24, 2009
Ford's New Car in India

Ford has pronounced that it is to make a latest car in India, as part of its $500m (£304m) investment plan in the country.
Manufacturing will begin on the Ford Figo at the carmaker's plant in Chennai in the first quarter of 2010.
Ford has described the Figo - which is Italian slang for "cool" - as a "game changer" and said it was confident it would be popular with Indian consumers.
The Figo will compete in India's small car segment, which makes up about 70% of the new vehicle market.
The car will initially only be for sale in India, but there are plans to export it to other countries, Ford said.
In April, the world's cheapest car, the Tata Nano, went on sale in India. The Nano is 10 feet (3 metres) long.
"[The Figo] reflects our commitment to compete with great products in all segments of this car market," said Ford president and chief executive Alan Mulally.

